Seat Belts
Wearing seat belts is the law. Always fasten your seat belt and make sure all your passengers are using seat belts or child restraints. Wearing seat belts (both lap belt and shoulder harness) will increase your chance of survival in most types of collisions. It is important to wear the seat belt correctly.
- A shoulder harness is worn across the shoulder and chest with minimal, if any, slack. The shoulder harness should not be worn under the arm or behind the back. Wearing the harness the wrong way could cause serious internal injuries in a collision.
- The lap belt should be adjusted so that it is snug and lies low across your hips after fastening. Otherwise, in a crash, you could slide out of the belt, resulting in injury or death.
- Pregnant women should wear the lap belt as low as possible under the abdomen, and the shoulder strap should be placed between the breasts and to the side of the abdomen’s bulge.
You and all passengers must wear a seat belt or you and/or your passenger(s) may be cited. If the passenger is under 16 years old, you may be cited if they are not wearing their seat belt.
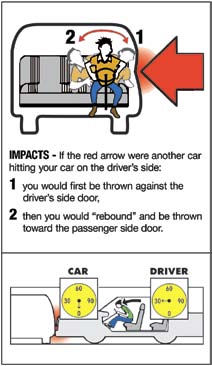
The graphic illustrates what can happen in a collision. If you are struck from the side, the impact could push you back and forth across the seat. Seat belts and shoulder harnesses keep you in a better position to control the vehicle and may minimize serious injuries. The graphic also illustrates how, when you collide, your vehicle stops, but you keep going at the same speed you were traveling, until you hit the dashboard or windshield.
Child Restraint System and Safety Seats
- Children under 2 years old must be secured in a rear-facing child passenger restraint system unless the child is 40 pounds or more, or 3 feet 4 inches or taller.
- Children under 8 years old, or who are less than 4 feet 9 inches tall, must be properly secured in a federally-approved child passenger restraint system.
- Children under 8 years old may ride in the front seat of a vehicle in a federally-approved child passenger restraint system under the following instances:
- There is no rear seat.
- The rear seats are side-facing jump seats.
- The rear seats are rear-facing seats.
- The child passenger restraint system cannot be installed properly in the rear seat.
- All rear seats are already occupied by children 7 years old or younger.
- Medical reasons require the child to not ride in the back seat.
- A child may not ride in the front seat of an airbag equipped vehicle if they are in a rear-facing child passenger restraint system.
- Children who are 8 years old or older OR who have reached at least 4 feet 9 inches in height may use a properly secured safety belt meeting federal standards.
Riding Safely With Air Bags
Air bags are a safety feature that help keep you safer than a seat belt alone. Ride at least 10 inches (measured from the center of the steering wheel to your breastbone) from the air bag cover, if you can do this while maintaining full control of the vehicle. If you cannot safely sit 10 inches away from the air bag, contact your vehicle dealer or manufacturer for advice about additional ways of moving back from your air bag.
Passengers should also sit at least 10 inches away from the passenger-side air bag.
Note: Children seated next to a side air bag may be at risk of serious or fatal injury.
Unattended Children in Motor Vehicles
It is never a good idea to leave a child unattended in a vehicle. It is illegal to leave a child 6 years old or younger unattended in a motor vehicle.
Note: The child may be left under the supervision of a person 12 years old or older.
Distracted Driving
- Visual—Eyes off the road.
- Cognitive—Mind off the road.
- Manual—Hands off the steering wheel.
Some actions that cause distracted driving and lead to vehicle collisions are:
- Using a handheld device (for example, cell phone, music device).
- Reaching for an object inside the vehicle.
- Looking at an object or event outside of the vehicle.
- Reading.
- Eating.
- Applying cosmetics (makeup).
More information regarding collisions and distractions can be found in the Driver Distractions (FFDL 28) Fast Facts brochure.
Hot Weather Risks
It is dangerous and illegal to leave children (CVC §15620) and/or animals in a hot vehicle. After sitting in the sun, even if a window is slightly opened, the temperature can rise rapidly inside a parked vehicle.
Dehydration, heat stroke, and death can result from overexposure to the heat. California Penal Code §597.7 prohibits leaving or confining an animal in any unattended motor vehicle under conditions that endanger the health or well-being of an animal due to heat.